This part of IEC 61850 describes the methodologies for the modelling of logics for IEC 61850 based applications in power utility automation. In particular, it describes the functional view of logic based on existing logical nodes for generic process automation and the operational modes of the logic. Furthermore it includes the specification of the standard language to be applied to specific the logic as well as the related data exchange format between engineering tools and their application as well as the mapping of logic elements to IEC 61850 data types.
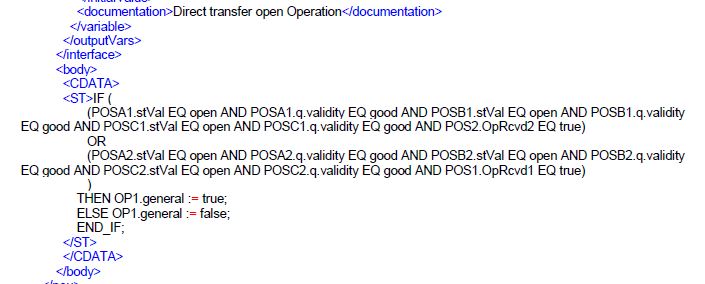
The IEC 61131-3 PLC programming language is used to describe syntax of functions.
Example PLD (Programmable Logic Description): The PLD file contains the logic unit program code in PLC OpenXML format, representing the description of the logic programmable scheme that can then be mapped to a GAPC LN instance. Excerpt:
- a Draft Technical Report (57/1817/DTR; 84 pages) with guidelines on how to apply IEC 61850 for substation automation: Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – Part 7-500: Basic information and communication structure – Use of logical nodes for modeling application functions and related concepts and guidelines for substations
This Technical Report of IEC 61850 describes the use of the information model for devices and functions of IEC 61850 in applications in substation automation systems but it may be used as informative input also for the modeling of any other application domain. In particular, it describes the use of compatible logical node names and data objects names for communication between Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED) for use cases. This includes the relationship between Logical Nodes and Data Objects for the given use cases. …
Part 7-5 describes in examples the use of logical nodes for modeling application functions and related concepts and guidelines in general independently from any application domain respectively valid for all application domains in the electric power system (substation automation, distributed energy resources, hydro power, wind power, etc.). This part 7-500 describes in examples the use of logical nodes for application functions in substation automation including also line protection between substations. It implies also some tutorial material where helpful. But it is recommended to read parts IEC 61850-5 and IEC 61850-7-1 in conjunction with IEC 61850-7-3 and IEC 61850-7-2 first.
- document for comments (57/1813/DC, 27 pages) on application profiles: Draft IEC TR 61850-7-6, Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – Part 7-6: Guideline for definition of Basic Application Profiles (BAPs) using IEC 61850
This guideline is focused on building Application / function profiles and specifies a methodology to define Basic Application profiles (BAPs). These Basic Application profiles shall provide a framework for interoperable interaction within or between typical substation automation functions. BAPs are intended to define a subset of mandatory features of IEC 61850 in order to increase interoperability in practical applications.
In the context of standards the term “profile” is commonly used to describe a subset of an entity (e.g. standard, model, rules).
Accordingly an IEC 61850 standard profile contain a selection of data models (mandatory elements), communication services applicable and relevant engineering conventions (based on the Substation Configuration Language SCL defined in IEC 61850-6) for an application function of a specific use case in the domain of power utility automation.
Depending on the scope and objective different profile types can be distinguished:
- User profile – defined subset that is valid for a specific user / organization (e.g. utility)
- Product / Device profile – implemented subset in a specific vendor product /device
- Domain profile – defined subset for a specific domain and relevant use cases (e.g. monitoring of substation)
- Application / function profile
A nice example is contained in Annex A:
Example for BAP of distributed automation function “reverse blocking” using BAP template. [blog.iec61850.com]